AI dermatology in action: How its diagnostic accuracy compares to dermatologists
Skin issues are the major reason for doctor visits all over the world. While everybody is concerned about skin lesions, not everybody has easy access to a dermatologist. Artificial intelligence (AI) brings a promising solution to this problem, with the image classification systems. Autoderm has taken a leading role in developing AI algorithms for skin lesion recognition, bridging the gap. A recent study explored the diagnostic accuracy of a deep learning model on the market made by Autoderm, using the Coachella dataset of 91 cases of skin lesions. The findings show how AI can diagnose skin lesions with an accuracy that is comparable to dermatologists, which can reshape the future of dermatology.
The importance of AI in dermatology is not limited to enhanced accessibility. It provides the perfect solution for other problems primary care physicians and dermatologists face, including time constraints and the overwhelming number of patients. It is estimated that 20% primary care patients see their physician, because of a dermatology concern. Another major benefit of using these AI tools for skin condition screening is rapid and accurate analysis, aiding early detection. They reduce manual workload, and improve diagnostic precision, fostering proactive skincare and treatment. For practical application of AI in real life patient diagnosis, it is important to make sure these algorithms have high accuracy. This study aims to compare the AI answers against dermatologists', quantifying its diagnostic accuracy.
Study Overview
A complete set of 91 images of various skin conditions were chosen as the study sample. These images, along with short descriptions of the location, color, size, and duration lesions, were reviewed by a group of board-certified dermatologists from the First Derm online platform who offered the most probable diagnosis according to the image and short history. These images were then run through the fully automated AI model, Autoderm V2_2, to get the top 5 suggestions it offered. These results were cross checked against the diagnoses given by the dermatologists in order to determine the accuracy and the sensitivity of the AI platform compared to the dermatologists' diagnosis.
Accuracy Assessment Metrics
- Top 1 accuracy: Top AI answer matches the correct diagnosis
- Top 3/ Top 5 accuracy: The correct answer appears within the top 3/top5 AI answer respectively
- Treatment accuracy: Accuracy of the treatment suggestion by AI, regardless of the answer given. (could be wrong answer, but correct treatment, in dermatology many diseases use the same treatment, like cortisone creams)
Data Analysis
Aggregate Data
A total number of 91 images were used for the study, consisting of 40 different skin conditions as diagnosed by board certified dermatologists through the First Derm platform. The following figure show the conditions grouped into different disease types, as identified by the AI and the dermatologists respectively.
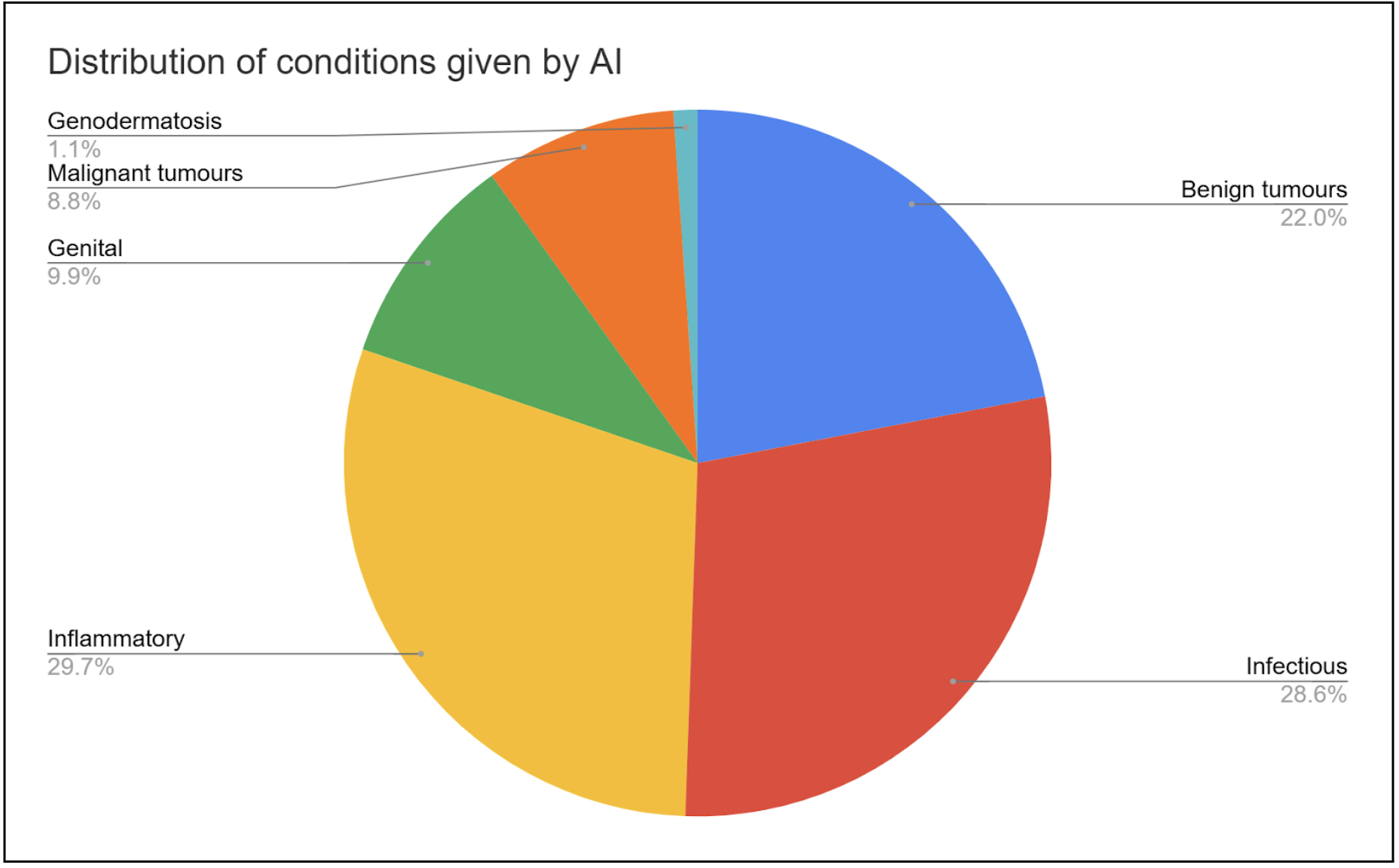
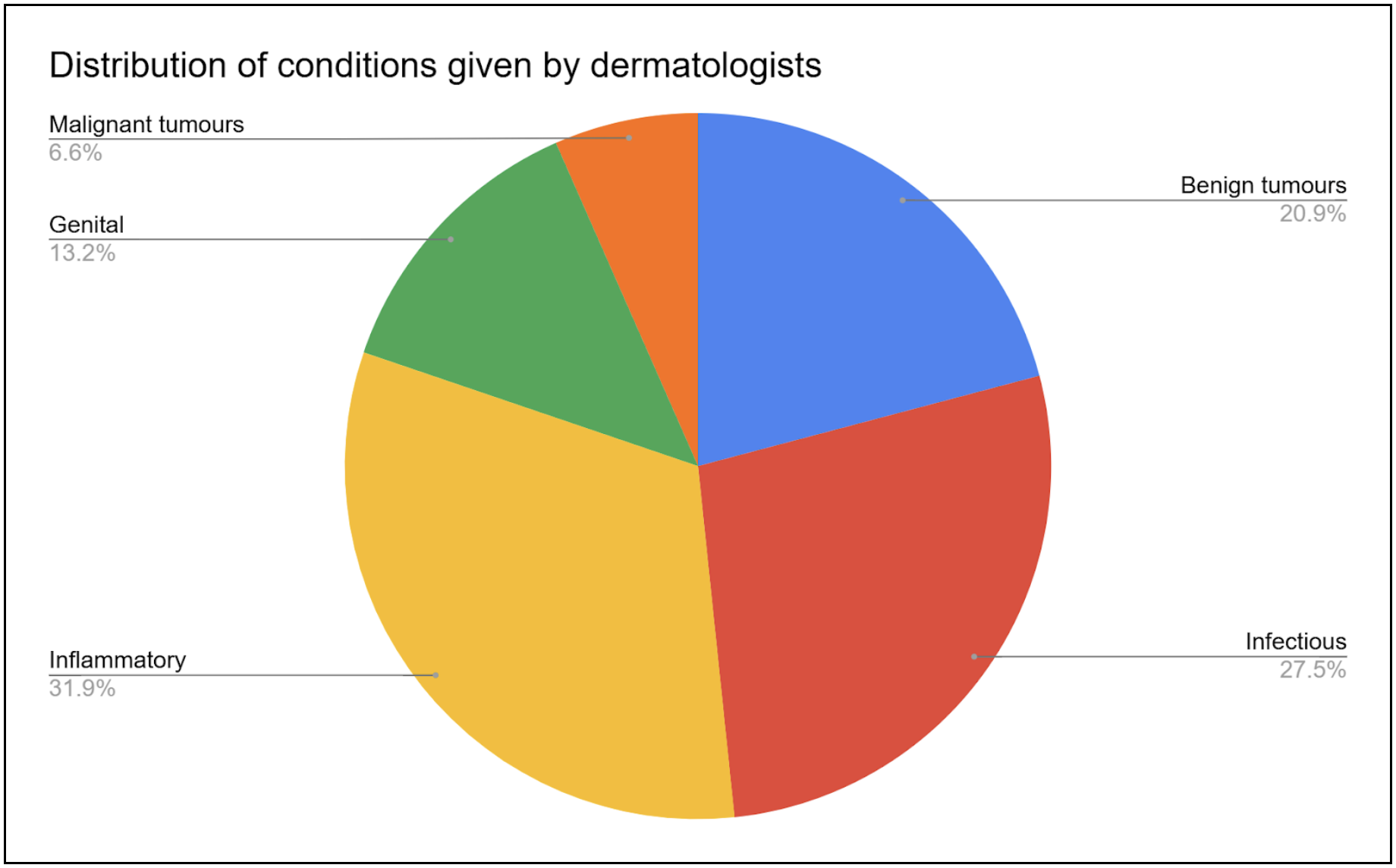
Diagnostic Accuracy: AI vs Dermatologists
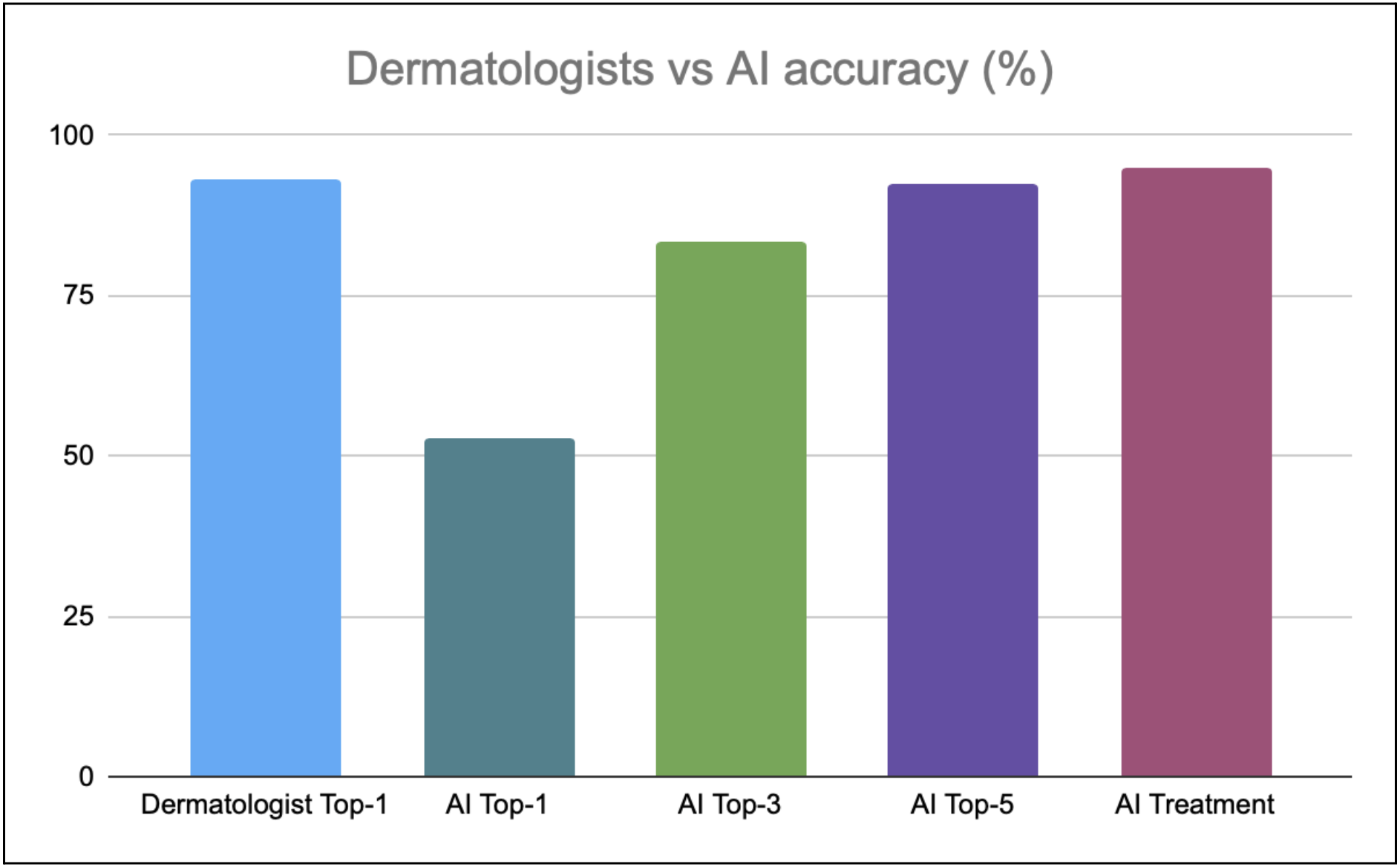
The overall accuracy of the AI model is significantly high, especially including the top 3 and top 5 predictions. The overall percentage accuracies of answers and treatment suggestions are summarized below.
Key Findings
Accuracy Results
- The First Derm online dermatologists were correct in 93% of cases.
- AI Top-1: 53%
- AI Top-3: 84%
- AI Top-5: 93%
- AI Treatment: 95%
While dermatologists outperform the AI by a considerable margin in the top 1 diagnostic accuracy, the gap is significantly reduced in top 3 and top 5 diagnostic accuracies. This highlights the importance of utilizing AI as a diagnostic aid, rather than as a replacement tool.
The accuracy of treatment recommendations is excellent. Despite giving the incorrect answer, the treatment recommendations were correct in 95% of the cases, highlighting its potential as a clinical aid in managing skin conditions.
Top 3 AI suggestions matched with the dermatologist's diagnosis in 84% cases. This high accuracy shows its potential as a triage tool.
Implications
Results suggest both patients and clinicians would benefit from integrating AI diagnostic models like Autoderm in clinical practice. This can be invaluable in a primary care setting to reduce time of consultation, reduce referral rates and assist the correct identification of the condition. Clinical input together with the AI expertise can ensure more favorable healthcare outcomes, reducing cost and increasing efficacy.
Limitations
The AI is not yet trained to give answers on some skin conditions, which hinders the comparison of those cases with dermatologists' diagnosis. It has been trained on 73 skin diseases, which represents about 95% of the common skin diseases that a normal patient would have.
The number of cases involved is relatively limited in scope. The dataset does not involve all the conditions the AI has answers to, which makes it impossible to determine the accuracy and sensitivity of the AI model in diagnosing those specific conditions. And there is only a small number of some diseases, making the measurements not very reliable for those individual cases.
AI performance depends on the image quality and the training data pool. The AI was not able to analyze any additional information (eg: location, color, size, and duration of the lesions) provided by the users which may have helped the dermatologists to arrive at the accurate diagnosis.
Since the AI results were compared to dermatologists' diagnoses offered via online platforms, there is a chance of the diagnosis that was taken as accurate over the AI suggestions to be faulty due to human error, in which case, the accuracy of the AI will be underestimated.
Conclusion
Recent AI models like Autoderm show promising potential to be utilized as a diagnostic assistant tool in dermatology. The significant diagnostic accuracy, rapid and consistent image analysis, accurate treatment suggestions and wide accessibility are the main strengths seen. Even though the AI system is not always perfect, there is a significant use of it as a screening tool. Also, there is potential for AI to develop into better versions with higher accuracy and higher sensitivity with future improvements.